Wednesday, December 17, 2014
Tree in data structure What is tree ?
What is tree
Definition:- Tree is is hierarchical (or non-linear) data structure.
or
Tree is a finite set of elements that is either empty or partitioned into three disjoint subsets ,the first subset contains a single element called the root of the tree.The other two subset are themselves tree called left and right subtree of original tree .Each element of tree is called a node of the tree .
Important Term related with trees-
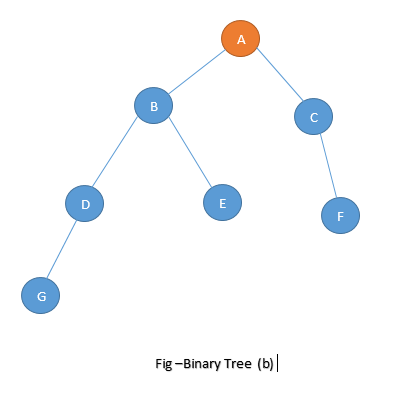
Root Node- The First Subset or single element called root or parent node of the tree (Such as A is the root node in above figure)
Leaf Node - The node that has no son is called leaf node of tree (Such as D,E,F,G are the leaf node in above fig)
Sibling- Two nodes are sibling if they have same parent (such as D,E and F,G are siblings)
Level of tree- The level of a node in binary tree is the number of edges traversed from the root node to the node i.e. root has 0 level and level of any other node is one more than the level of its parents (such as level of below tree is 3 )
Depth of Tree- The depth of tree is the maximum level of any leaf in the tree ( such as depth of below tree is 4)
Climbing- Going from the leaves to the root is called "climbing"
Descending - Going from the root to the leaves is called descending
Types of Tree in data structure -Binary Tree Lecture 2
Types of Binary Trees?What are the different type of Binary Tree?
Types of Binary Trees
1. Strictly Binary Tree-
- If Every non leaf node in binary tree has non empty left and right subtrees ,the tree term as strictly binary tree .
Important Point for Strictly Binary Tree-
- Every non-leaf node has degree 2
- A strictly binary tree with n leaves has (2n -1 ) nodes
- Thus strictly binary tree has odd number of nodes
2. Complete Binary Tree -
- A complete Binary tree of depth d is the strictly binary tree whose all leave are at level d
- A Complete Binary Tree of depth d is the binary tree that contains exactly 2^l (two ki power l nodes )
- Issi prakar kisi bhi complete Binary tree (CBT) mein total no of nodes (2^d+1 -1) where d is depth of tree
- Isse ek conclusion ye nikalta hai ki complete Binary Tree hamesha Strict Binary tree hogi but strict binary tree hamesha complete binary tree (CBT) nhi hogi
- Jaisa ki hum jante hai CBT Hamesha Strict Binary tree hogi tab agar iske n leaves honge to isme total no of nodes 2n-1 honge
Tuesday, December 16, 2014
What is Binary tree,Different type of tree in Data structure
Different type of tree in Data structure
Binary Tree:-
- A Binary tree is a finite set of elements that is either empty or is partitioned into three disjoint subset
- The First subset contains a single element called the root of the tree
- The other two subsets are themselves binary tree ,called left and right subtrees of the original tree.
- Each element of a binary tree called a node of the tree
Friday, December 5, 2014
MCQ of DBMS fundamental question
MCQ Data Base Management System on Basic Fundamental
Q1.A Specific example where physical data independence would not hold is
- When data file is changed from unordered file to sorted file
- When additional access structure (Example an index ) is created for relation
- When DBA decides to store the data in B+ tree
- When the user writes an application program to join tables
Q2.Integrity means________
- Protecting the data against unauthorized users
- Protecting data against authorized users
- Making sure users are allowed to do the thing they are trying to do
- None of These
Q3.Controlling redundancy in database management system help to
- Avoid duplication of effort
- Avoid unnecessary wastage of storage space
- Avoid Inconsistence among data
- All of the above
Q4. Which of the following function not performed by DBA?
- Planning ,designing ,and implementation of database system
- Allocation of storage locations and data structures
- Establishing standards and procedures system
- Communicating with data base users
Q5.Which of the following is not an advantages of database approach ?
- Elimination of the data redundancy
- Ability to associate related data
- increased security
- All of the above
Q.6 A data Dictionary doesn't provides information about
- Where data is located
- The size of the disk storage
- Who owns or responsible for the data
- How data is stored
Q7.The data base administrator is ,in effects ,the coordinator between the _____and the ____
- DBMS ; database
- Application program ; Database
- Database ;Users
- Application programs ;Users
Q.8 Which of the following is not usually part of the responsibilities of a DBA?
- Approving Structure changes to the database
- Designing data entry screens
- Ensuring that an adequate backup regime is in place
- Issuing Accounts to users and monitoring the performance of the system
- Physical keys ,but the relation model is faster because it uses logical keys.
- Logical keys ,
Saturday, September 27, 2014
What is RDBMS Lecture -4
What is RDBMS
DBMS:-
Data base management system (DBMS) which follows all the 12 rule given by Dr Edgar F. Codd known as Relational data base management system (RDBMS)
According to Dr.Edgar F codd rule are as follows
1 Information Rule :-
This rule states that all information (data) ,which stored in database must be stored in table formats,this information can be user data or meta -data.
2.Guaranteed Access rule :-
This rule states that every single data element (value) is guaranteed to be accessible logical with combination of table name and primary key .
3.Systematic Treatment of NULL value:-
This rule states that NULL value in the database must be given systematic treatment i.e. primary key value never be NULL because NULL have several meaning that cause various anomaly occurs in data base
4.Active online catalog :-
This rule states that the structure of whole database must be stored in an online catalog i.e. Data Dictionary
5. Comprehensive data sub-language rule :-
This rule states that database must have support for a language which has linear syntax which is capable of Data Definition ,Data Manipulation,Data control
6.View Updating rule:-
This rule states that all system should able to updates all views of database without any anomaly in the system
7. High-level insert -Update and Delete rule:-
This rule states that system must support high level insertion,updation ,deletion this must not be limited to a single row that it must support join operations to yield set of data
8. Physical data independence:-
This rule states that application should not have any concern about ,how the data physically stored in the system as well as any change in physical structure must not have any impact on application
9.Logical Data Independence:-
This rule states that logical data must be independent of its user's view as well as any change in logical data must not imply any change in the application .e.g. if two table are merged or one is split into two different table there should be no impact on the application
10.Integrity Independence:-
This rule states that all integrity constraints can be independently modified without the any change in the application.this rule makes database independent of front-end application and its interface.
11.Distribution Independence:-
This rule states that the end user must not be able to see that the data in distributed over various locations,end user have feel that data is located at one site only.
12. Non-subversion rule:-
This rule states that if system has an interface that provides access to low level records ,this interface then must not be able to subvert the system and bypass security and integrity constraint
DBMS Data Independence Lecture -3
Data Independence
Data independence can be define as the capacity to change the schema at one level of data base system without having to change the schema at higher level .data independence further classified into to category as follow
1.Logical Data Independence
2.Physical data Independence
Logical data Independence:-
The capacity to change the conceptual Schema without having to change the external schema or users programs
Physical data Independence:-
The capacity to change the the internal Schema without having to change the conceptual schema
Database Management system (Advantage of DBMS over flat file system) Lecture -2
Unknown2:25 AMDatabase Management system(Advantage of DBMS over flat file system) Lecture -2
No comments

Advantage of DBMS over flat file system
2.Gives less I/O task to Access data
3. It gives more concurrency level
4.More Security over the data File [By providing Views]
5. Data Independence [By providing three level Interdependency]
6.Data Integrity and Security
7.Data Administration
8.concurrent Access and crash recovery
9.Control Redundancy [Duplication of data]
10.Reduced Application Development time [By providing Higher level Interface]
Click Here for previous Lecture -1
Tuesday, September 16, 2014
Data Base Management System Made easy class room note Lecture -1
Data Base Management System Made easy class room note Lecture -1
DBMS syllabus and reference for GATE
Databases:
Relational model (ER-model, relational algebra, tuple calculus), Database design (integrity constraints, normal forms), Query languages (SQL), File structures (sequential files, indexing, B+ trees), Transactions and concurrency control;
Reference Book:-
Database system concepts – > Silberschatz , Korth , Sudarshan
Database systems – > C.J.Date (Normalisation is very lucidly written )
Principles of Database Systems – > J.D.Ullman (This is a very good book )
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note:-
As per analysis of GATE previous years papers found that all the topics of the above syllabus are important so i suggest you go through all the topic but as per previous GATE paper experience probability of occurring question are more from -Normalization,normal form relation algebra, SQL query and transactions and concurrency .
Once you will go through old paper you will find that maximum time 2 question (link question) asked from SQL query only or normalization (normal form) and one marks question from rest of the syllabus so focus on these two topics so in our lecture we will cover these topic first .
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is DBMS?
Before understand DBMS we understand some basic terminology
Database:- Database is a collection of related data
Management System:- A software used to manage the database in efficient way
DataBase+Management Syatem =DBMS
DBMS Definition:- Database is a computer base record keeping system and the way through which we manage the system known as management system
DBMS Definition by Korth:-
A Database management system is a collection of interrelated data and set of programs to access these data.
DBMS Defination by Ullman:-
DBMS is powerful tool for creating and managing large amount of data efficiently and allowing it to persist over long period of time.
Saturday, September 13, 2014
Introduction of Java Programming (Basic Introduction) Lect-1
Introduction of Java Programming
Key Note :-
- Before start Java programming you have to understand that how to learn java ,what strategy required to learn java because there are lot of book available in market/Internet for java which only provides you content but no book tell us that how to start /how to read /what are the right track for learning java programming
- Second point which comes in your mind that to learn java what kind of programming background required i.e. whether C/C++ mandatory to learn before start java .
- I frankly tell you that for java there is no need of background knowledge of C/C++,but if know its fruitful for you.
- The next thing comes to your mind that why Java where various programming language available in the market?
- Java is Almost pure object oriented /platform independent programming language.which support concept of WORA(Write once run any where)
- Later on I will give many reason why java only
Tuesday, June 17, 2014
Introduction of java Lect-2
Introduction of java Lect-2
What is Java?
Java is Pure Object Oriented platform Independent (Architecture neutral) Language developed by James Gosling from Sun Micro system(sun)in 1991. The first publicly available version of Java (Java 1.0) was released in 1995.
Note:- Java technology is both a programming language and a platform.
Note:- Sun Microsystems was acquired by the Oracle Corporation in 2010
Note:- Over time new enhanced versions of Java have been released.
Note:- The current version of Java is Java 1.7 which is also known as Java 7
Note:- From the Java programming language the Java platform evolved.
Note:- The Java platform allows software developers to write program code in other languages than
the Java programming language.
History of Java Language
- In 1991 a group of Sun Microsystems engineers Led by James Gosling ,decided to develop a Language for consumer device (Like- cable Box, Microwave ,Washing Machine etc)
- They Wanted the language to be small because these device don’t’ have powerful CPU.
- They also wanted the language to be hardware independent since different manufactures would use different CPU.
- The project was Name Green….
- They decided to compile the code to an intermediate machine like code for imaginary CPU called Virtual Machine (VM),actually there is a real CPU,that implement this virtual CPU
- This intermediate code called Byte Code
- Byte code Completely Hardware Independent
Thursday, January 23, 2014
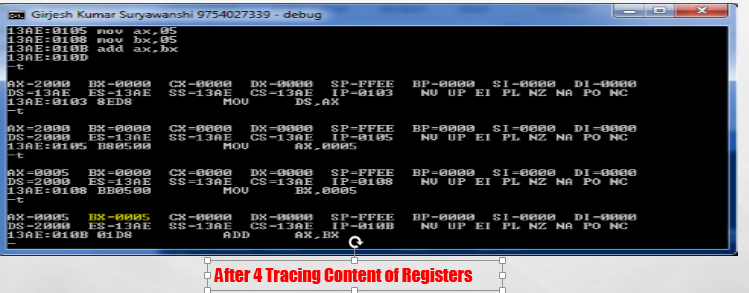
step by step procedure to perform addition of two number in Assembly language using debugger Lecture-3
Lecture -3
Addition Program in Assembly Langauage
step by step procedure to perform addition of two number in Assembly language using debugger..
Note :-If you want to do Assembly Language programming then you to follow following Step
step:-1
Open Command prompt type debug and press enter


step:-2
After pressing enter type (a) to change debugger into assembly language mode
step:-3
Step:-4 Initialize data Segment
Step:-5
Step:-6
Step:-7
Step:- 8 Perform tracing by pressing t continue and view content of registers
Tuesday, January 21, 2014
Introduction of assembly language Lecture -2
Introduction of assembly language Lecture -2
Lecture -2
Assembly Language:-
In Assembly language mnemonic code (ADD, SUB, MUL)
are used in place of large machine instruction.so user don't have to remember large
set of instruction for performing different operation. e.g.
5 101
+ 5 ADD 101
--------- --------------------
10 1010
Note :-If you want to do Assembly Language programming then you to follow following Step
step:-1
Open Command prompt type debug and press enter

step:-2
After pressing enter type (a) to change debugger into assembly language mode
Learn C programming online/ Learn C programming in 21 Days
Learn C programming online
Lecture -1
Basic Understand of Computer and its Language
Note:-If any one want to start learn "c" Programming then He/She have to remember following things.
- First very important that It required patience in you.
- Keen Interest for programming .
- You to ask question that from where we have to start .
- What is the right way to learn C programming .
- It doesn't Requires Any Coaching ,the thing which is required is your effort.
- How Important It is .
- Be-live me if you learn "C" then you don't need to learn any other language.
- There are lot of books available in market for "c" ,but not a single book which tell us that how to read and learn
- Here i will provides you step by step procedure to learn "c" Programming.
Step :-1
Understand the Definition of Computer/What actually Computer is?
Definition:-
Computer is a Electronic device ,which takes Data and Instruction as input from user and perform processing over it and generates desire output.Here i want to coin out some term like data (fact,figure,information,from user)and instruction indicates what operation computer have to perform over input data and How it have to perform.
Needs of Languages:-
like in Human being if they want to communicate with each other they required a common language which is understand by both the party,then only communication is possible.
Same as If you want to communicate with Computer (M/C) you have to communicate in computer language i.e. Machine language (0101010)...
Note :- So What you think which language is used first to communicate with computer
Machine language only..
Machine Language:-
Machine Language also called Low level language in which binary number
(010101) is used to write instruction for computer.
for example if you want to write simple program for addition of two number then
suppose
you want to perform addition of 5 and 5 then first you have to provide
binary equivalent of five to machine and then instruction for addition
which again written in machine language .e.g.
Figure :-1
Machine Language Programming Have various advantage And Disadvantages
Advantages of Machine Language:-
- Execution time of program is very less Because it doesn't Requires any translator.
- Better Hardware Interaction Because it close to Hardware.
- Provide Real time Interaction to the users.
Disantages of Machine Language:-




















.jpg)